Ham Temperature Oven: Achieving the ideal internal temperature for perfectly cooked ham is crucial for both food safety and flavor. This guide delves into the science and art of cooking ham in the oven, providing essential information on safe temperature ranges, cooking methods, and troubleshooting common issues. From selecting the right thermometer to understanding the impact of ham size and oven type, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to consistently produce delicious and safe results.
Whether you’re preparing a bone-in ham for a holiday feast or a spiral-sliced ham for a weeknight dinner, mastering the intricacies of oven cooking ensures a succulent and safe meal. This comprehensive guide covers everything from pre-cooking preparation to reheating leftovers, providing step-by-step instructions and valuable tips for achieving ham perfection every time.
Safe Ham Temperatures
Achieving the perfect ham requires understanding safe internal temperatures. Undercooking can lead to foodborne illnesses, while overcooking results in a dry, tough product. This section details safe temperature guidelines for various ham types and the consequences of improper cooking.
Safe Internal Temperatures for Different Ham Types
The following table provides recommended internal temperatures for different types of ham, ensuring food safety and optimal texture.
| Temperature (°F) | Ham Type | Cooking Method | Safety Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 145°F | Fully Cooked Ham (Pre-cooked) | Reheating | Reheat to ensure an even internal temperature. Discard if left at room temperature for more than 2 hours. |
| 155°F | Bone-in Ham (Uncooked) | Baking/Roasting | Ensure the thickest part of the ham reaches this temperature. |
| 155°F | Spiral-Sliced Ham (Uncooked) | Baking/Roasting | Because of the slicing, this type of ham cooks faster. Use a meat thermometer to ensure even cooking. |
Consequences of Improper Ham Cooking
Undercooking ham can lead to bacterial contamination, potentially causing food poisoning. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. Overcooking, on the other hand, dries out the ham, making it tough and less palatable. The ideal cooking method ensures the ham reaches a safe temperature while maintaining its moisture and flavor.
Ham Temperature and Cooking Time Relationship
The relationship between ham temperature and cooking time is directly proportional to the ham’s weight. A larger ham requires a longer cooking time to reach the safe internal temperature. The following visual representation would show a graph with cooking time on the x-axis and internal temperature on the y-axis. Separate lines would represent different ham weights (e.g., 4-6 lbs, 6-8 lbs, 8-10 lbs), illustrating that heavier hams require longer cooking times to reach the target temperature of 155°F.
The graph would clearly show the linear relationship between weight and cooking time needed to achieve food safety.
Oven Cooking Methods for Ham
Several oven cooking methods can be used to prepare ham, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice depends on the type of ham, desired outcome, and available time.
Comparison of Oven Cooking Methods
Baking, roasting, and glazing are common methods for cooking ham in the oven. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Baking:
- Advantages: Simple, consistent cooking.
- Disadvantages: Can result in drier ham if not monitored carefully.
- Roasting:
- Advantages: Allows for browning and crisping of the ham’s surface.
- Disadvantages: Requires more attention to prevent burning.
- Glazing:
- Advantages: Adds flavor and visual appeal.
- Disadvantages: Can burn easily if not carefully monitored.
Step-by-Step Guide for Baking a Bone-in Ham
- Preheat oven to 325°F (160°C).
- Place ham in a roasting pan.
- Add 1 cup of water or broth to the bottom of the pan to prevent drying.
- Bake for approximately 15-20 minutes per pound, or until a meat thermometer inserted into the thickest part registers 155°F (68°C).
- Let rest for 10-15 minutes before slicing and serving.
Flowchart for Cooking a Spiral-Sliced Ham
A flowchart would visually represent the steps involved in cooking a spiral-sliced ham, emphasizing temperature checks at key stages to ensure food safety. The flowchart would begin with preheating the oven, then proceed to placing the ham in the oven, checking the internal temperature at regular intervals (e.g., every 30 minutes), and finally, removing the ham from the oven once it reaches 155°F.
The flowchart would include decision points, such as whether the ham has reached the safe temperature, and would clearly indicate the next step based on the decision.
Monitoring Ham Temperature During Cooking: Ham Temperature Oven
Using a reliable meat thermometer is crucial for ensuring the ham reaches a safe internal temperature and avoids undercooking or overcooking. Accurate temperature monitoring guarantees food safety and optimal ham quality.
Importance of Using a Meat Thermometer
A meat thermometer provides an accurate reading of the ham’s internal temperature, eliminating guesswork and ensuring food safety. Unlike relying on visual cues, a thermometer offers precise measurement, preventing undercooking which can lead to foodborne illness.
Proper Thermometer Insertion
Insert the meat thermometer into the thickest part of the ham, avoiding bone or fat. Ensure the probe is fully inserted to obtain an accurate reading. The thermometer should be placed in the center of the ham, away from any areas that might be influenced by external heat sources or uneven cooking.
Troubleshooting Tips for Ham Cooking
- Uneven Cooking: Rotate the ham halfway through the cooking time to ensure even heat distribution.
- Temperature Inconsistency: Use a reliable meat thermometer and check the temperature in multiple locations to ensure uniform cooking.
- Overcooked Ham: Reduce cooking time or oven temperature for subsequent attempts. Consider using a lower temperature and longer cooking time for more even results.
Factors Affecting Ham Cooking Time and Temperature
Several factors influence the cooking time and temperature of a ham, including its size, type, and starting temperature. Understanding these factors allows for accurate adjustments and optimal cooking results.
Influencing Factors on Ham Cooking, Ham Temperature Oven
The size and type of ham significantly affect cooking time. Larger hams require longer cooking times to reach the safe internal temperature compared to smaller hams. Pre-cooked hams require only reheating, while uncooked hams need to be cooked to a safe internal temperature. The starting temperature of the ham also impacts cooking time; a colder ham will require more time to cook than one that is already partially cooked.
Oven Type Influence

Source: instructablesrestaurant.com
Convection ovens cook faster than conventional ovens due to their enhanced air circulation. Adjust cooking times accordingly when using a convection oven. A convection oven will typically reduce cooking time by 25%, but it is crucial to monitor the internal temperature with a meat thermometer to ensure food safety.
Adjusting Cooking Time and Temperature
Adjustments to cooking time and temperature should be based on the specific characteristics of the ham. For example, a larger bone-in ham will require a longer cooking time at a lower temperature to ensure even cooking and prevent overcooking. Always use a meat thermometer to guide these adjustments and ensure the ham reaches the safe internal temperature.
Ham Reheating and Storage
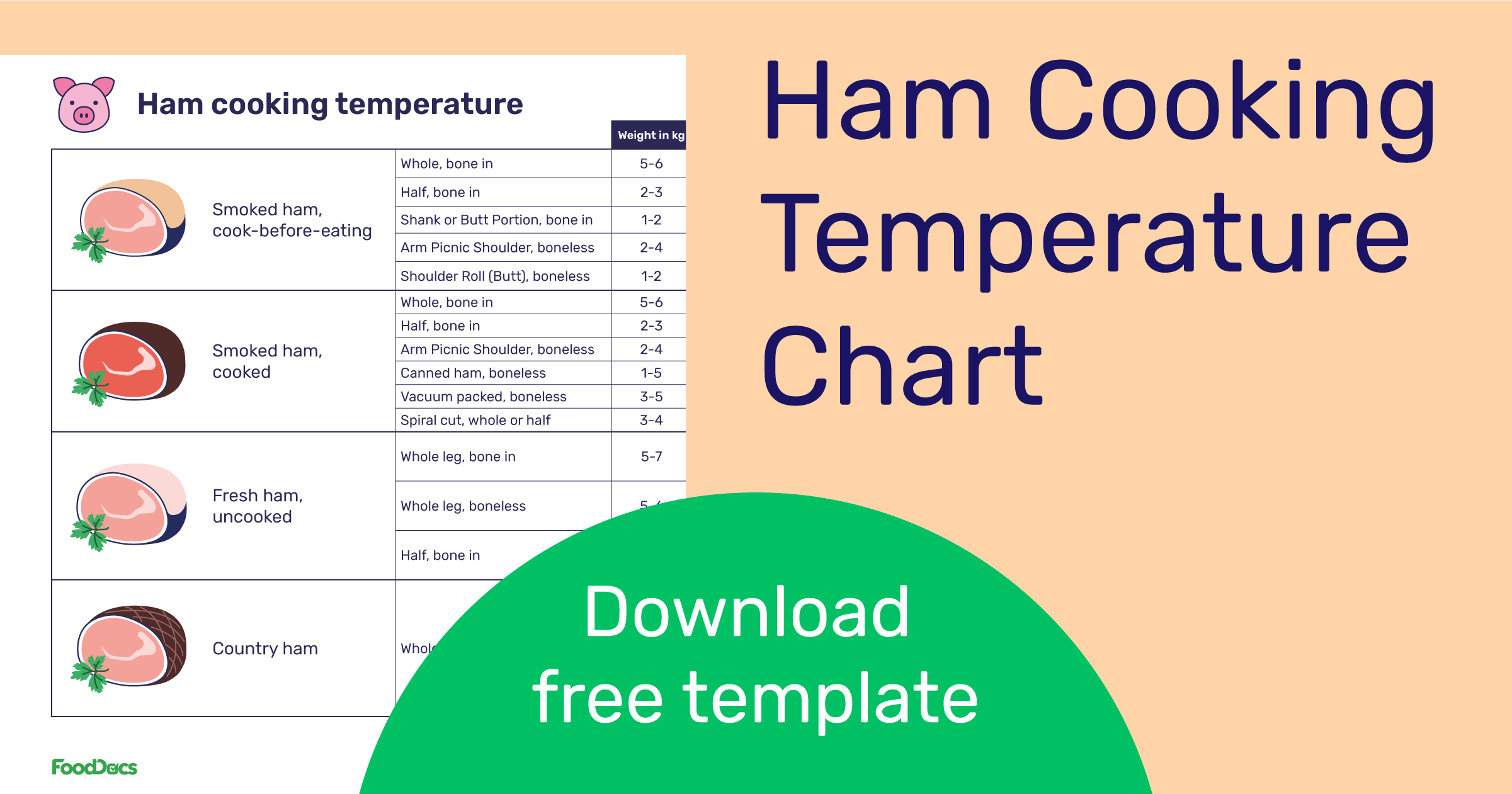
Source: fooddocs.com
Proper reheating and storage methods are essential for maintaining the quality and safety of leftover ham. Following these guidelines helps prevent bacterial growth and ensures the ham remains palatable.
Safe Ham Reheating Methods
- Preheat oven to 325°F (160°C).
- Place leftover ham in an oven-safe dish.
- Cover the dish with foil to retain moisture.
- Reheat until the internal temperature reaches 140°F (60°C).
Proper Ham Storage
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of cooked ham. Refrigeration is essential to slow down bacterial growth and prevent spoilage.
Achieving the perfect ham requires precise oven temperature control; a crucial aspect often overlooked by home cooks. Understanding the nuances of this process is akin to the spiritual depth explored in Kendrick Lamar’s recent work, as detailed in this insightful article: Kendrick Lamar Faith. Both require careful attention to detail and a deep understanding of the underlying principles for optimal results, ensuring a succulent ham or a meaningful spiritual journey.
Recommended Storage Times and Temperatures
| Storage Method | Temperature | Maximum Storage Time | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 40°F (4°C) or below | 3-4 days | Store in an airtight container or tightly wrapped in plastic wrap. |
| Freezer | 0°F (-18°C) or below | 2-3 months | Wrap tightly in freezer-safe wrap or foil to prevent freezer burn. |
Conclusive Thoughts
Cooking ham to the perfect temperature is a delicate balance of science and culinary skill. By understanding the factors that influence cooking time and temperature, utilizing a reliable meat thermometer, and following safe reheating and storage practices, you can consistently achieve delicious and safe results. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, empowering home cooks to confidently prepare flavorful and safe ham dishes for any occasion.
