IRS Tax Relief Credit offers significant financial assistance to eligible taxpayers. Understanding these credits can mean substantial savings, or even a larger tax refund, at tax time. This guide breaks down the eligibility requirements, different credit types, and the process of claiming these valuable deductions, empowering taxpayers to navigate the complexities of tax relief.
From the Child Tax Credit to Earned Income Tax Credit, numerous programs exist to help alleviate the tax burden for families and individuals meeting specific criteria. Knowing which credits you qualify for and how to claim them correctly is crucial for maximizing your tax benefits. This comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge to navigate this often-confusing process.
IRS Tax Relief Credit Eligibility Requirements
Understanding eligibility for IRS tax relief credits is crucial for taxpayers seeking to reduce their tax burden. Eligibility hinges on several factors, including income levels, filing status, and qualifying life events. These credits are designed to provide financial assistance to individuals and families facing specific challenges.
General Eligibility Criteria
General eligibility for IRS tax relief credits often involves meeting specific requirements related to income, filing status, and the nature of the qualifying event. For instance, many credits have income limits, meaning only those below a certain threshold can claim them. Filing status (single, married filing jointly, etc.) also impacts eligibility, as do specific qualifying events, such as having a dependent child or experiencing a significant medical expense.
Income Limitations and Requirements
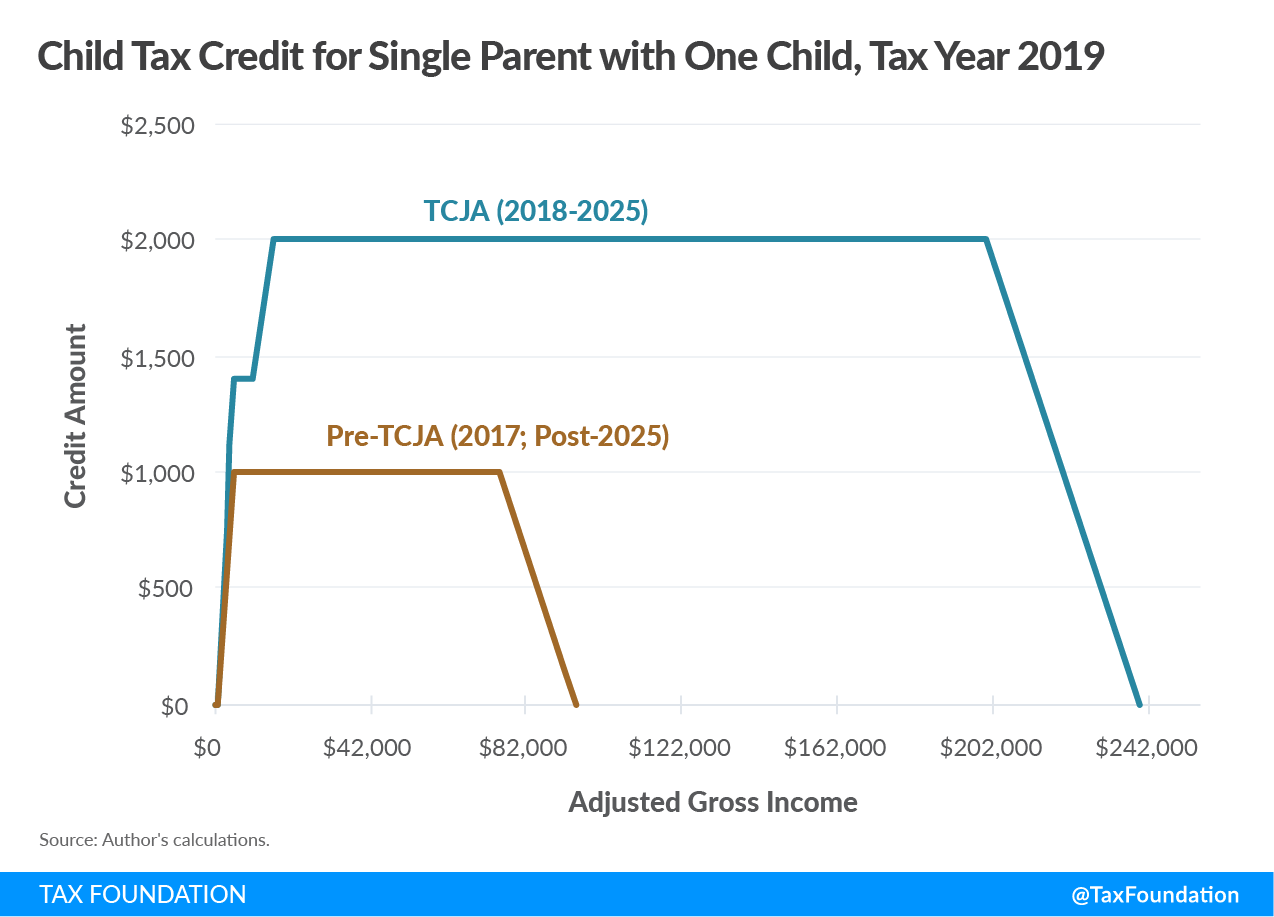
Income limitations vary significantly across different tax relief credits. Some credits are phased out gradually as income rises, meaning the credit amount decreases as income increases, eventually reaching zero above a certain income threshold. Others have a sharp cutoff, where no credit is available once income surpasses a specific limit. It’s essential to consult the IRS guidelines for the specific credit you’re interested in to understand the applicable income limits.
Qualifying Life Events
Several life events can make individuals eligible for various tax relief credits. These include having a qualifying child or dependent, incurring significant medical expenses, experiencing a natural disaster, or facing unemployment. The specific event and its documentation requirements will determine the applicable credit.
Examples of Tax Relief Credits
| Credit Type | Eligibility Criteria | Income Limits | Example Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Child Tax Credit | Qualifying child under age 17, US citizen or resident alien | Phased out above certain income levels | Family with two qualifying children, income below the phaseout threshold. |
| Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) | Low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families | Varies based on income, filing status, and number of qualifying children | Single parent with one qualifying child, working part-time. |
| American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) | Student pursuing higher education | Income limits apply; maximum credit amount is limited | Student attending college, with income below the limit. |
| Child and Dependent Care Credit | Expenses for childcare to allow work or job search | Income limits apply; maximum credit amount is limited | Working parent paying for daycare for their child while at work. |
| Saver’s Credit | Low-to-moderate-income taxpayers contributing to retirement accounts | Income limits apply; maximum credit amount is limited | Low-income taxpayer contributing to a traditional IRA. |
Types of IRS Tax Relief Credits
The IRS offers a variety of tax relief credits designed to assist taxpayers in different circumstances. Understanding the nuances of each credit is critical for maximizing potential tax savings. Each credit has specific requirements, documentation needs, and limitations.
The IRS Tax Relief Credit offers crucial financial assistance to eligible taxpayers, but navigating the complexities can be challenging. Understanding housing costs is key to maximizing this credit, and a helpful resource for assessing local rental rates is the rentamarket website. This data can help individuals accurately calculate their eligible expenses and ensure they receive the full amount of IRS Tax Relief Credit they deserve.
- Child Tax Credit (CTC): Provides a credit for qualifying children. Income limits apply, and the credit amount may be reduced or phased out for higher-income families.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): A refundable credit for low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families. Eligibility depends on income, filing status, and number of qualifying children.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC): Helps pay for higher education expenses for eligible students. There are income limits and maximum credit amounts.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit: Provides a credit for expenses paid for the care of qualifying children or other dependents to allow the taxpayer to work or look for work.
- Saver’s Credit: Incentivizes saving for retirement by offering a credit for contributions to retirement accounts. Income limits apply.
Claiming the IRS Tax Relief Credit
Claiming a tax relief credit involves accurately completing the relevant sections of your tax return and providing supporting documentation. Accurate record-keeping is essential to avoid delays or potential penalties.
Steps to Claiming a Tax Relief Credit
- Gather all necessary documentation, such as W-2s, 1099s, childcare receipts, and other relevant forms.
- Carefully review the instructions for the specific credit you are claiming.
- Complete the appropriate forms and schedules, accurately reporting all required information.
- Attach all supporting documentation to your tax return.
- Electronically file or mail your tax return to the IRS.
Common Errors to Avoid
- Inaccurate reporting of income or expenses.
- Failing to meet all eligibility requirements.
- Missing supporting documentation.
- Incorrectly completing the tax forms.
Impact of IRS Tax Relief Credits on Tax Liability

Source: alleviatetax.com
Tax relief credits directly reduce a taxpayer’s tax liability. This reduction can result in a smaller tax bill or even a refund. The amount of the reduction depends on the specific credit claimed and the taxpayer’s overall tax situation.
Illustrative Example, Irs Tax Relief Credit
Let’s say a taxpayer owes $5,000 in taxes. If they qualify for a $1,000 tax credit, their tax liability is reduced to $4,000. If the credit is refundable, they might even receive a $1,000 refund, reducing their tax liability to $0.
Resources for Finding More Information on IRS Tax Relief Credits
Source: taxfoundation.org
Several resources offer comprehensive information on IRS tax relief credits. These resources provide detailed explanations of eligibility requirements, claiming procedures, and contact information for assistance.
IRS.gov The official website of the Internal Revenue Service provides detailed information on all tax credits, including eligibility requirements, claiming procedures, and frequently asked questions.
Publication 970, Tax Benefits for Education This IRS publication provides comprehensive information on tax credits for education expenses, including the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit.
IRS Taxpayer Assistance Center The IRS operates Taxpayer Assistance Centers (TACs) nationwide, providing in-person assistance with tax questions and issues.
Potential Pitfalls and Misconceptions Regarding IRS Tax Relief Credits
Several misconceptions and potential pitfalls can lead to incorrect claims or missed opportunities for tax relief. Understanding these issues can help taxpayers avoid problems and ensure they receive the credits they are entitled to.
- Misunderstanding eligibility requirements: Carefully review all requirements to ensure you qualify for the credit.
- Inaccurate record-keeping: Maintain meticulous records of all expenses and income to support your claim.
- Failing to file on time: Missing the tax deadline can result in penalties and lost opportunities.
- Fraudulent claims: Falsely claiming a credit can result in significant penalties and legal consequences.
Illustrative Example: A Family Claiming the Child Tax Credit
The Johnson family, with two qualifying children under age 17, has an adjusted gross income (AGI) of $60,000. They are eligible for the Child Tax Credit. Assuming the current CTC amount per child is $2,000, their total credit would be $4,000. This would directly reduce their tax liability by $4,000. They would use Form 1040, Schedule 8812 (Form 1040), Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents, to claim the credit.
Summary: Irs Tax Relief Credit
Successfully navigating the IRS Tax Relief Credit system requires careful planning and accurate record-keeping. By understanding eligibility requirements, choosing the appropriate credit, and meticulously completing the necessary forms, taxpayers can significantly reduce their tax liability and potentially receive a substantial refund. Remember to utilize available resources and seek professional assistance if needed to ensure a smooth and successful tax filing experience.
